Describe ways to represent data – Describe core data concept
Skill 1.1: Describe ways to represent data
In the world of data, the way information is structured and organized plays a crucial role in its effective management and utilization. There are three fundamental ways you can repre-sent data: structured, semi-structured, and unstructured. Each representation offers unique
1
characteristics and brings its own set of opportunities and challenges to the realm of data management.
By understanding these different ways to represent data, you and your organization can make informed decisions on how to store, process, and analyze your data effectively. Each data representation method offers distinct advantages and is suited to specific use cases. Whether it’s the structured precision of relational databases, the flexibility of semi-structured data, or the untapped potential of unstructured data, embracing these representations empowers you to unlock the full value of your data assets.
This skill covers how to:
- Describe features of structured data
- Describe features of semi-structured data
Describe features of structured data
Structured data is a well-organized format that follows predefined schemas, providing efficient storage, retrieval, and analysis. It represents information in a tabular form with clear relation-ships between entities, making it highly suitable for relational databases. The structured nature of this data allows for easy sorting, searching, and querying using Structured Query Language (SQL). Examples of structured data include financial transaction records, customer profiles, and inventory management systems.
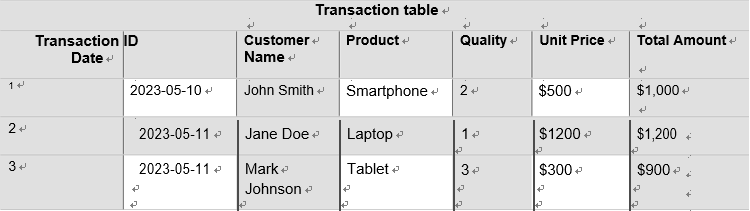
Imagine you have a structured data table representing sales transactions in a retail business. The table would have columns such as Transaction ID, Date, Customer Name, Product, Quality, and so on, as shown in Table 1-1. Each row would represent a specific sale, with corresponding values in each column. The structured format allows you and others in the business to effi-ciently track sales, analyze customer behavior, and generate insights for decision-making.
TABLE 1-1 Structured data
- CHAPTER 1 Describe core data concept
Structured data provides organizations with a consistent and organized way to store and manage critical information. It ensures data integrity and facilitates relational operations so you can perform complex queries, generate reports, and derive meaningful insights. Relational databases, such as Azure SQL Database, provide robust and scalable solutions for storing and processing structured data in a structured query language.
